Revolutionizing Automotive Safety: The Rise of High-Tensile Strength Sheets
The automotive industry in India is set for remarkable growth, driven by increasing demand, technological advancements, and supportive government policies. Projections indicate significant market expansion in the coming years, with the industry expected to become the third largest in the world by 2026. As the industry evolves, the focus on enhancing vehicle safety and performance becomes paramount. A critical area of development is the use of high-tensile strength sheets in the forming segment, offering superior safety and impact resistance.
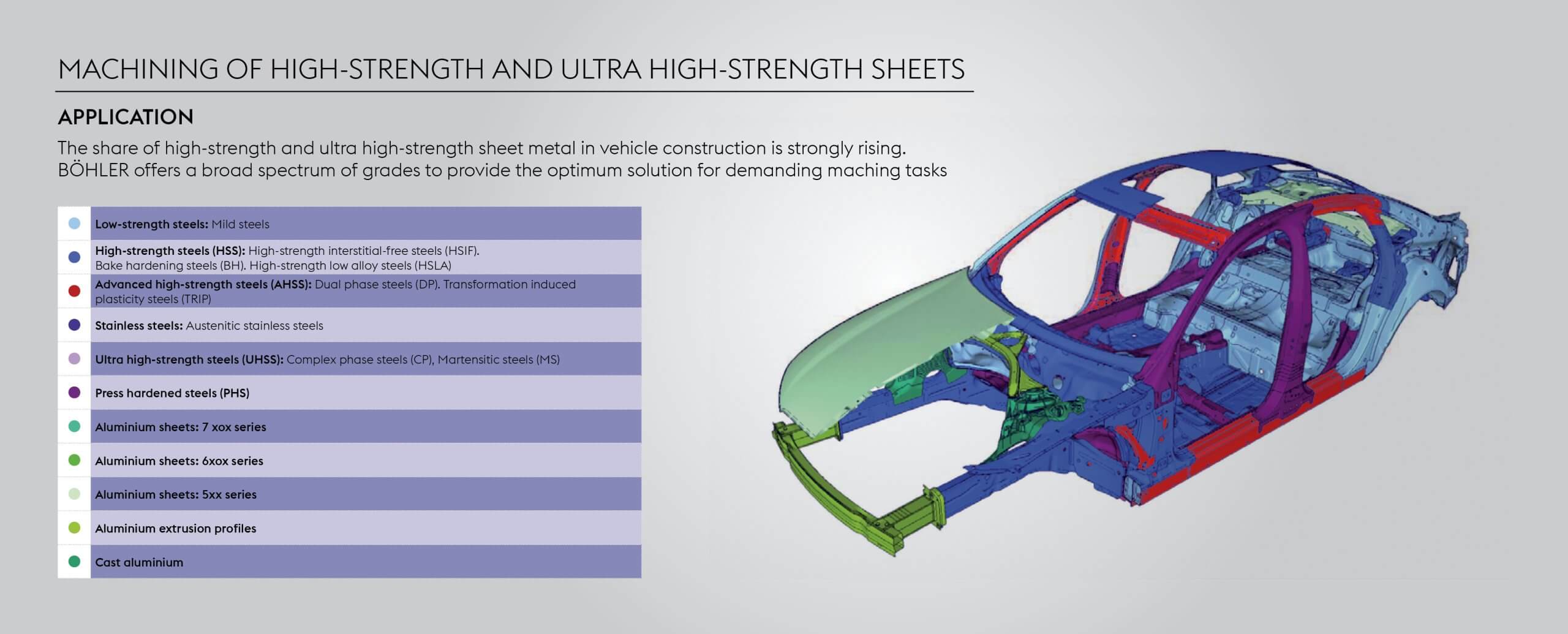
High-tensile strength sheets are becoming essential in automotive manufacturing due to their exceptional strength and durability. These sheets are designed to absorb and distribute impact energy during accidents, significantly improving passenger safety. The industry’s emphasis on lightweight yet robust materials make high-tensile strength sheets an ideal choice.
High-tensile strength sheets provide excellent performance in various automotive applications, including body panels, chassis, and structural components. They offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and fatigue durability, ensuring long-term reliability and safety. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting these materials to meet stringent safety standards and consumer expectations.
Trends and Future Requirements
The demand for high-tensile strength sheets is expected to rise as the automotive industry continues to innovate and prioritize safety. Future trends include the development of even higher strength materials, improved formability, and advanced manufacturing techniques to produce complex shapes and components. Innovations such as hot stamping, where sheets are heated to high temperatures and then rapidly cooled in a die, are becoming more prevalent. This process increases the material’s strength and allows for the creation of intricate geometries.
Innovations in High-Tensile strength Sheet Manufacturing and Application
Recent advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as hot stamping and roll forming, have enabled the production of high-tensile strength sheets with superior properties. Innovations in material science, including the use of alloying elements and heat treatments, have further enhanced the performance of these sheets.
Hot Stamping: This process involves heating steel sheets to over 900°C before forming and quenching them in a die. The rapid cooling results in ultra-high strength, making it ideal for A-pillars, B-pillars, and side door beams in a car.
Roll Forming: This continuous bending operation forms high-tensile strength sheets into desired shapes with high precision and minimal waste. It’s particularly useful for long parts with uniform cross-sections, such as side impact beams.
Overview of Safety Regulations in the Automotive Industry
Safety regulations in the automotive industry are becoming increasingly stringent, with new norms aimed at enhancing vehicle safety and reducing fatalities. These regulations mandate the use of advanced materials and technologies to improve crashworthiness and protect passengers.
New and Upcoming Norms
- Bharat New Vehicle Safety Assessment Program (BNVSAP): This program sets stringent crash test standards for vehicles sold in India. It includes frontal and side-impact tests, pedestrian protection, and child occupant protection. The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways is also working on several other safety regulations. These include the introduction of driver drowsiness detection systems, blind-spot detection systems, and lane departure warning systems.
- Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP): India is introducing its own vehicle safety standards called the Bharat NCAP, which will assign star ratings to vehicles based on their safety and sturdiness, similar to the Global NCAP and European NCAP programs. This initiative aims to enhance road and vehicle safety by encouraging manufacturers to incorporate advanced safety features.
- Pedestrian Protection Regulations: These regulations require automakers to design vehicles that minimize injury to pedestrians in the event of a collision. High-tensile strength sheets help achieve this by deforming in a controlled manner to absorb impact energy.
High-tensile strength sheets play a crucial role in meeting these safety requirements. Traditionally, automotive companies used sheets with tensile strengths of around 600 MPa, usually made from High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steels. However, there has been a shift towards Partial Martensitic steels with tensile strengths ranging from 1000 to 1200 MPa. This change is driven by the need for materials that provide better impact resistance and safety during accidents. These high-tensile strength sheets are particularly important for critical structural components such as A-pillars, B-pillars, and side door beams. Their ability to absorb and distribute impact energy makes vehicles safer for occupants and pedestrians.
Impact on Tooling Industry
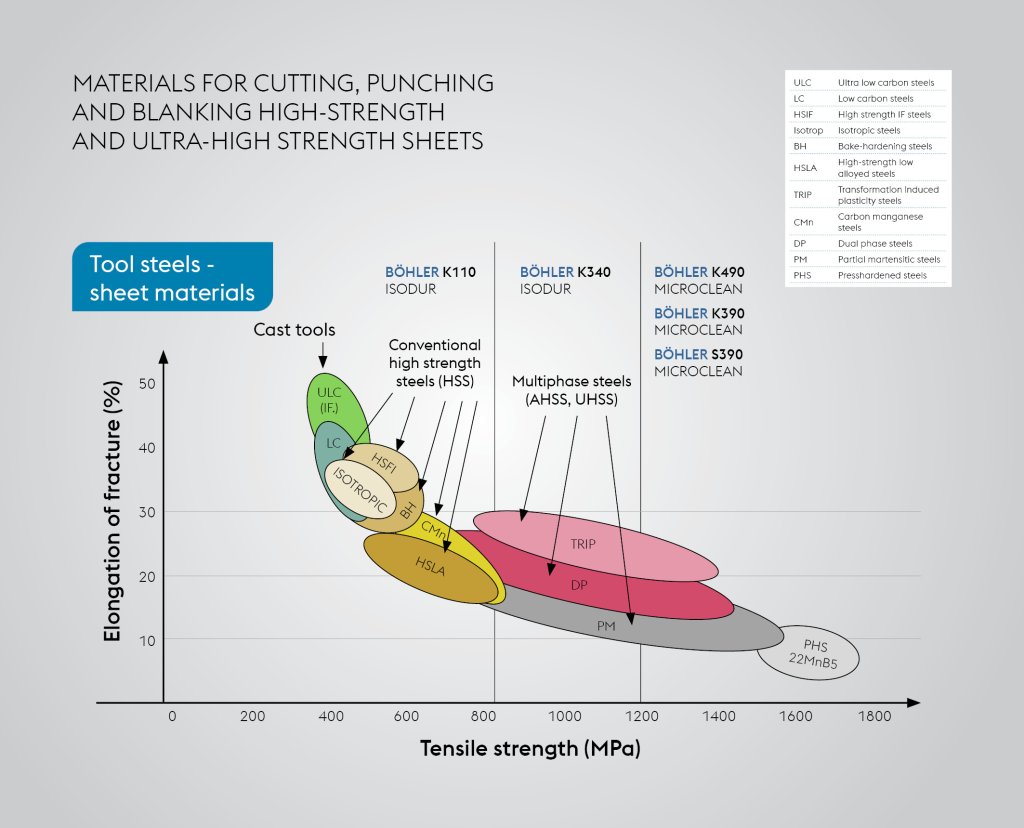
The shift towards high-tensile strength sheets necessitates significant changes in tool and die manufacturing. Conventional steels like D2 or 1.2379 are often inadequate for forming high-tensile strength sheets, leading to increased wear and reduced tool life. To address these challenges, the industry is moving towards powder metallurgical (PM) steels, which offer superior performance and durability.
Upgrading to PM steels is essential for efficient and cost-effective production of high-tensile strength sheet components. PM steels provide better wear resistance, toughness, and thermal stability, enabling longer tool life and reduced maintenance. This transition enhances production efficiency and ensures consistent quality of formed parts.
Comparison between Conventional and PM Steels
Conventional tool steels like D2 or 1.2379 are prone to wear and deformation when used with high-tensile strength sheets, leading to frequent tool changes and downtime. In contrast, PM steels offer enhanced properties that make them ideal for high-stress applications. They exhibit higher hardness, improved wear resistance, and better fatigue performance, making them suitable for the demanding conditions of automotive forming processes.
Benefits of Using PM Steels
Using ESR/PM steels for tooling and dies offers several benefits, including:
- Increased tool life and reduced maintenance costs
- Enhanced precision and consistency in part production
- Improved overall productivity and efficiency
- Better quality of formed components, leading to improved vehicle safety and performance.
Conclusion
The automotive industry’s focus on safety and performance is driving the adoption of high-tensile strength sheets in the forming segment. These materials offer superior strength and impact resistance, aligning with the industry’s stringent safety regulations and evolving requirements. As manufacturers transition to high-tensile strength sheets, the need for advanced tool and die solutions becomes paramount. PM steels are crucial in meeting these demands, ensuring efficient production and high-quality components. The future of the automotive industry lies in the continued innovation and application of high-tensile strength sheets, paving the way for safer, more efficient vehicles.
BÖHLER provides advanced ESR/PM steels such as BÖHLER K340 ISODUR, K390PM, K490PM, and S390PM, which are essential for the effective forming of high-tensile strength sheets in automotive applications.